Antipyretic Analgesics:
- Salicylates ( e.g. Aspirin, Methyl salicylates )
- Acetanalide ( e.g. Paracetamol , known in the US as acetaminophen or simply APAP )
- Anthranilic acid derivatives ( e.g. Ponstan )
- Opioid drugs such as morphine and oxycodone
Salicylates:
Salicylic acid it self used as potent analgesic but has gastric irritation so the derivative of salicylic acid are produced to reduce the gastric toxicity .Derivative of salicylic acid are the salts of carboxyl group as well as acetyl derivative of salicylic acid.
Aspirin ( Acetyl salicylic acid , Dispirin )
Methyl salicylates ( Wintogeno balm )
Aspirin: ( Acetyl Salicylic acid )
Brand name : DispirinActive Ingredient : Aspirin
IUPAC name : Methyl 2- hydroxybenzoate
Molecular formula : C8H8O3
Structural formula of Dispirin : Aspirin + Na -citrate + NaHCO3
Synthesis:retic analgesics

To control the toxicity of Aspirin:
To overcome the toxicity , prepare the salt by the substituting the H+ OF - COOH group with Na+, Mg 2+ , Al 3+, Ca 2+ etc
By giving the anti-acid like Calcium Glutamate
e.g. Bufferin = Aspirin + Calcium glutamate
Dispirin = Aspirin + Na-citrate + NaHCO3
It has vasodilator and also have mild hypotensive activity . It is used in cardiovascular disease .
Pre-coated Aspirin ( Ascard ) used to avoid the gastric irritation.
Dispirin = Aspirin + Na-citrate + NaHCO3
It has vasodilator and also have mild hypotensive activity . It is used in cardiovascular disease .
Pre-coated Aspirin ( Ascard ) used to avoid the gastric irritation.
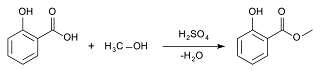
Methyl Salicylate :
Brand name: Wintogeno balm
Active ingredient : Methyl Salicylate
IUPAC name : Methyl 2-hydooxy benzoate
Molecular formula : C8H8O3
Botanical Background:
Methyl salicylate is naturally produce from many species of plants . Plants which produce methyl salicylate is called wintergreen. Some species of the genus Gaultheria in the family , Ericaceae . Some species of the genus Betula in the family Betulaceae.Synthesis :
Uses of Methyl Salicylate:
- Chewing gum and candies
- As a solvent for insecticides
- Used to provide fragrance to various products like detergents and perfumes
- Used in toothpaste , ink , polish and soft drinks
- Used as an anti-freezing agent
Side effects:
Kidney damage and smooth infections.

Comments
Post a Comment